In the dynamic landscape of modern business, a robust marketing strategy is the compass guiding companies towards success. Let’s break down this critical process into three key steps, each pivotal in achieving your business objectives.
There are many frameworks to plan your marketing. Like most beginner marketers, I tried all and didn’t like them because they looked good on slides but not in real-world use. So I made my own.
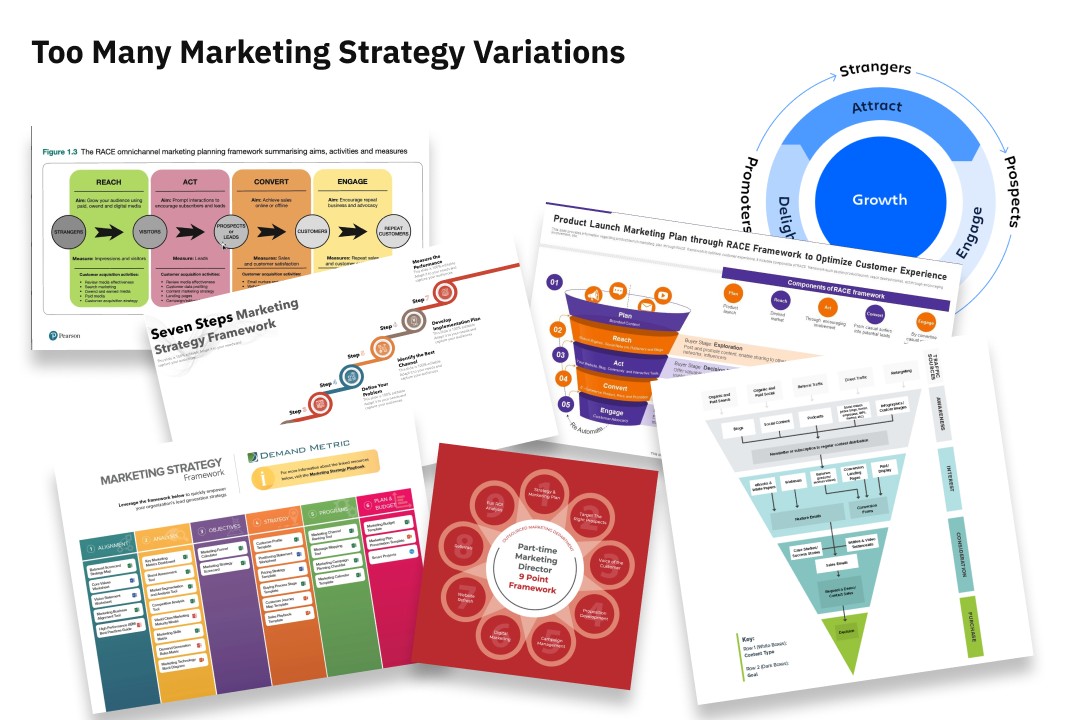
In this post, we’ll focus on the ‘Atomic Marketing Strategy Approach’, which is simple (but not always easy). The key to getting it right is iteration. With every iteration comes clarity.
Usually, it takes up to 3-4 weeks to develop the initial Marketing Strategy.
Use case: As a B2B Marketing Agency, we start our clients with a Marketing Strategy. This way, we’ll understand the full picture of the client is offering and how we can plan their marketing activities.
Advantages of Atomic Marketing Strategy
Why should you adopt the Atomic Marketing strategy
- Most marketing strategy was written in silos without help from other departments. Atomic Marketing Strategy invites collaboration from other departments, design teams, product teams, finance, procurement, and sales support (anyone who can chip in)
- Focus on Clients. Atomic Marketing Strategy follows the clients. It will always be centred around clients. In short, we deliver marketing right to the right prospect and are not too focused on our products.
- Iterative Planning. As a new opportunity, new media, and new trend emerges, the Atomic Marketing strategy can help the team to stay on their toes and add new information. At the same time, remains central to the idea, the customer comes first.
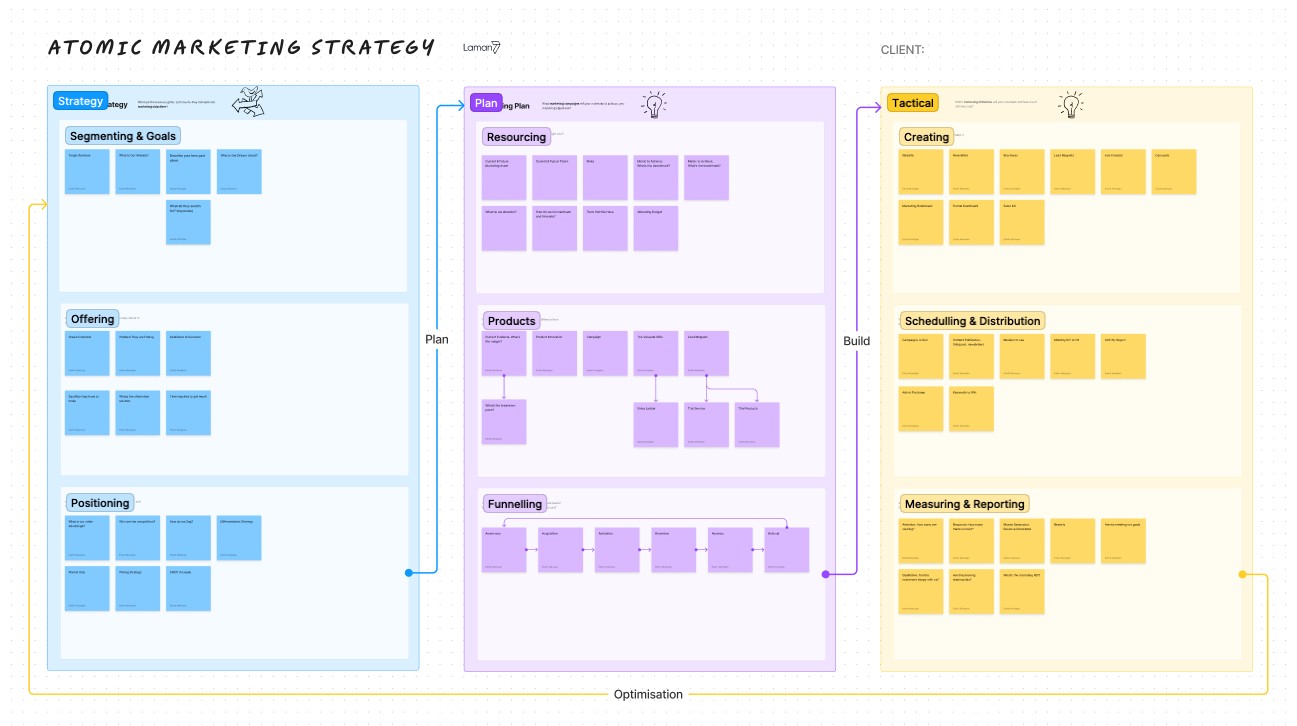
Step 1: Atomic Marketing Strategy – Segmentation, Offering, Positioning
In the initial phase, defining your target audience through segmentation and identifying your ideal customers’ specific demographics, behaviours, and needs are crucial. Most of your time should be spent researching past clients, market outlook and competition.
Segmentation
Start by dividing your target market into segments based on demographics, psychographics, and behaviours. Leverage tools like CRM software to collect and analyze customer data, allowing you to understand their preferences, purchase history, and engagement patterns.
What are the problems being faced, by whom, and of those, who can you – and do you want to – help?
Offering
Craft a compelling product or service offering tailored to the identified segments. Utilize product management tools to streamline development processes and customer feedback surveys to gather insights. This iterative approach ensures that your offerings align with customer needs and expectations.
What products and services do you offer to help clients to overcome their problems?
Positioning
Establish a unique market position by defining your value proposition. Conduct thorough competitor analysis using tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to identify gaps and opportunities. Implement brand tracking software to monitor how your brand is perceived, allowing you to refine your positioning strategy based on market dynamics.
What are the competencies, capabilities, experiences, and opinions that enable you to differentiate your firm?
Do consider rejecting certain positions that your company no longer carries.
Utilize tools like Google Analytics for audience insights, customer surveys, and competitor analysis tools to refine your segmentation, offering, and positioning strategies.
Step 2: Atomic Marketing Plan – Resourcing, Products, Funnelling
With a solid strategy, proceed to the marketing plan, focusing on finding, educating, and channelling your audience. Finding involves reaching your target audience through various channels.
The bulk of the time is spent planning the resources. The question of ‘who will do this’ to deliver the marketing campaign often pops up but if you have a B2B Marketing Agency partner, they will do all the planning and execution for you.
Resourcing
In the context of marketing strategy, “resourcing” refers to allocating and managing various resources, including financial, human, and technological assets, to effectively implement and support the marketing initiatives of a business.
Resourcing is critical in ensuring a company’s marketing strategy is executed efficiently and yields the desired results.
- Financial Resources: Allocating budgetary resources is a fundamental aspect of resourcing in marketing. This involves determining how much money is available for marketing activities, such as advertising, promotions, events, and digital campaigns. Adequate financial resourcing ensures that marketing goals are supported without exceeding budget constraints.
- Human Resources: The personnel responsible for implementing the marketing strategy are a key resourcing component. This includes marketing professionals, designers, content creators, analysts, and other team members. The right mix of skills and expertise is crucial for executing diverse marketing tactics and campaigns.
- Technological Resources: Marketing in the modern era often relies on various technologies, from customer relationship management (CRM) systems to marketing automation tools and analytics platforms. Resourcing involves selecting, implementing, and managing these technologies to streamline marketing processes and enhance efficiency.
- Time Resources: Time is a valuable resource in marketing, and resourcing involves setting realistic timelines for executing different marketing activities. Efficient time management ensures that campaigns are launched on schedule and that the marketing strategy aligns with broader business timelines and objectives.
- Data and Information Resources: Access to accurate and relevant data is crucial for making informed marketing decisions. Resourcing in terms of data involves acquiring, managing, and utilizing data sources to gain insights into customer behaviour, market trends, and the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
The common pitfall of most Marketing is not having the right person to execute the marketing. Do consider Marketing as a Service on top of in-house hire.
Products
In Atomic Marketing Strategy, “products” refer to the goods or services a company offers to its target market. Products are a central marketing mix component, including price, place, and promotion.
Developing a successful marketing strategy involves careful consideration of the product itself, its features, benefits, branding, and how it meets the needs and desires of the target audience. Here’s a breakdown of the role of products in marketing strategy:
- Product Development: Marketing strategy begins with developing products that align with the needs and preferences of the target market. This involves understanding customer requirements, conducting market research, and creating offerings that provide unique value or solve specific problems.
- Product Features and Benefits: The features and benefits of a product are critical elements of its marketing strategy. Marketers need to communicate what sets the product apart, how it addresses customer pain points, and the positive outcomes or experiences it offers.
- Branding: Branding is the process of creating a unique and recognizable identity for a product. It involves establishing a brand image, values, and positioning that resonates with the target audience. Effective branding contributes to customer loyalty and differentiation in the market.
- Product Life Cycle: Products go through various stages in their life cycle, including introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. Understanding where a product is in its life cycle helps marketers make informed decisions about pricing, promotion, and distribution strategies.
- Product Positioning: Product positioning involves how a product is perceived concerning competing products in the market. Marketers strive to position their products as offering unique benefits or characteristics that make them the preferred choice among target customers.
- Product Mix and Portfolio Management: Companies often offer a range of products to cater to diverse customer needs. Managing the product mix involves deciding which products to invest in, promote, or phase out based on their performance and contribution to overall business goals.
- Packaging and Presentation: How a product is packaged and presented can significantly impact consumer perception. Packaging protects the product and is a powerful marketing tool, conveying information about the brand and influencing purchasing decisions.
- Product Quality and Customer Satisfaction: Ensuring product quality is essential for building and maintaining customer trust. Satisfied customers are more likely to become repeat buyers and advocates for the brand, contributing to long-term business success.
- Innovation and Adaptation: The market is dynamic, and successful marketing strategies involve continuous innovation and adaptation of products to meet changing customer preferences, technological advancements, and industry trends.
- Product Pricing: Pricing is a critical element of the marketing mix. The price of a product must reflect its perceived value in the eyes of the customer while also considering competitive pricing, cost structures, and overall business objectives.
Funnelling
Guide your audience through the buyer’s journey by strategically channelling them from awareness to conversion. Use AAARRR Marketing Funnel to channel your prospect from a stranger to becoming your client.
Here’s a quick recap of AAARRR Funnel
- Awareness (A) How can we inform potential customers of our brand or product?
- Acquisition (A)Question: How do we convert interested individuals into leads and potential customers?
- Activation (A) – How can we turn leads into actively engaged users or customers?
- Retention (R) – How can we keep customers engaged and encourage repeat business?
- Revenue (R) – What strategies can be implemented to maximize the monetary value of each customer?
- Referral (R) – How can we turn satisfied customers into advocates who bring new business?
By addressing these questions at each stage of the AAARRR funnel, businesses can develop a comprehensive marketing strategy that attracts and acquires customers, retains them, and turns them into loyal advocates, contributing to sustained business growth.
How will you get their attention, build trust and create leads? What’s the message, offer and which medium do we use?
Step 3: Atomic Tactical Plan – Creating, Scheduling, Distribution & Measurement
The final step involves executing your strategy with a tactical plan. Create compelling content that aligns with your brand and resonates with your audience.
In the tactical phase, emphasis is placed on execution. Having identified the individuals responsible for the tasks, the execution process tends to flow seamlessly, as roles are clear and responsibilities have been assigned efficiently.
Creating
“Creating” in Atomic marketing strategy involves the development of various marketing assets that collectively contribute to the success of a product or service in the market. These assets encompass visual, written, and experiential elements designed to engage and resonate with the target audience. Let’s explore how “creating” is translated into different marketing assets:
- Content Assets:
- Blog Posts and Articles: Crafting informative and valuable written content to educate and engage the audience.
- Videos and Infographics: Developing visually appealing assets for conveying information in an easily digestible format.
- Whitepapers and Ebooks: Creating in-depth resources that showcase industry expertise and thought leadership.
- Campaign Assets:
- Social Media Posts: Designing and sharing compelling content across social media platforms to drive campaign objectives.
- Email Marketing Campaigns: Creating visually appealing emails with impactful messaging to reach and convert target audiences.
- Ad Creatives: Designing visuals and copy for online and offline advertisements to promote campaigns.
- Brand Assets:
- Logo Design: Crafting a memorable and distinctive logo representing the brand identity.
- Brand Guidelines: Developing a comprehensive set of guidelines that ensure consistency in brand visuals and messaging.
- Brand Storytelling: Creating a compelling narrative communicating the brand’s values and mission.
- Product or Service Assets:
- Product Packaging: Designing visually appealing and informative packaging for physical products.
- User Guides and Manuals: Creating instructional materials that enhance the user experience of a product or service.
- Product Demos: Developing interactive demonstrations to showcase product features and benefits.
- Visual and Graphic Design Assets:
- Website Design: Crafting visually appealing and user-friendly website layouts.
- Marketing Collaterals: Designing brochures, flyers, and other print materials that align with the brand’s visual identity.
- Visual Branding Elements: Creating consistent visual elements such as color schemes, typography, and imagery.
- Social Media Content Assets:
- Visual Posts: Designing visually appealing images and graphics for social media sharing.
- Video Content: Creating engaging videos tailored to the platform and target audience.
- Interactive Content: Developing quizzes, polls, and other interactive assets to encourage audience participation.
- Event and Experience Assets:
- Event Branding: Creating visuals and promotional materials for events that align with the brand.
- Workshop Materials: Developing engaging presentations and materials for workshops and training sessions.
- Virtual Event Experiences: Crafting immersive online experiences for virtual events, webinars, and live streams.
In short, “Creating” in marketing strategy involves producing diverse assets that collectively contribute to a cohesive and compelling brand presence in the market. Each asset serves a specific purpose within the marketing strategy, aiming to attract, engage, and retain the target audience effectively.
Scheduling
“Scheduling” in marketing strategy refers to the strategic planning and organization of various marketing activities over time. This involves setting timelines, determining the frequency of campaigns, and optimizing the timing of promotional efforts to maximize impact and reach the target audience effectively. Here’s a breakdown of the role of “scheduling” in the context of marketing strategy:
- Content Calendar:
- Objective: Plan and organize the creation and publication of content across different channels.
- Implementation: Develop a content calendar outlining the schedule for blog posts, social media updates, newsletters, quiz marketing and other content types. Ensure consistency and alignment with overall marketing objectives.
- Campaign Timelines:
- Objective: Strategically time the launch and duration of marketing campaigns for maximum impact.
- Implementation: Create detailed timelines for each marketing campaign, considering factors such as product launches, seasonal trends, and industry events. Coordinate across channels to optimize reach.
- Email Marketing Schedule:
- Objective: Optimize the timing of email campaigns to enhance open rates and engagement.
- Implementation: Determine the most effective days and times for sending marketing emails based on the target audience’s behavior. Experiment with A/B testing to refine the schedule. E
- Social Media Posting Schedule:
- Objective: Establish a consistent and effective posting schedule on social media platforms.
- Implementation: Identify peak times when the target audience is most active on each platform. Utilize scheduling tools to plan and automate posts, maintaining a regular presence and engagement.
- Ad Campaign Timing:
- Objective: Time the launch and duration of paid advertising campaigns to maximize visibility.
- Implementation: Consider factors such as peak shopping seasons, competitor activities, and audience behavior when scheduling online and offline ad campaigns. Monitor and adjust the schedule based on performance metrics.
- Product Launch Schedule:
- Objective: Coordinate the timing of product launches to generate maximum interest and sales.
- Implementation: Develop a comprehensive schedule for product launches, including pre-launch teasers, launch day promotions, and post-launch follow-ups. Align the schedule with other marketing activities to create a cohesive strategy.
- Webinar and Event Schedule:
- Objective: Plan and schedule webinars, workshops, and events for optimal audience participation.
- Implementation: Select suitable dates and times for virtual or in-person events, considering the target audience’s availability and time zones. Promote events well in advance to generate interest.
- SEO and Content Updates:
- Objective: Regularly update and optimize website content for search engine performance.
- Implementation: Establish a schedule for reviewing and updating website content to align with SEO best practices. Schedule regular blog posts, product updates, and other content releases to maintain relevance.
- Customer Communication Schedule:
- Objective: Maintain regular communication with customers to foster engagement and loyalty.
- Implementation: Develop a schedule for customer communications, including newsletters, updates, and personalized messages. Ensure timely responses to customer inquiries and feedback.
- Budget Allocation Timeline:
- Objective: Plan the allocation of marketing budgets across campaigns and activities.
- Implementation: Create a timeline for budget allocations, considering seasonal trends, campaign priorities, and business goals. Regularly review and adjust the budget schedule based on performance and market dynamics.
Effective scheduling in marketing strategy ensures that activities are coordinated, resources are optimized, and campaigns are executed precisely. It involves a proactive and dynamic approach, adapting schedules based on real-time data and market insights to achieve the desired outcomes.
Measuring and Reporting
“Measuring and Reporting” in Atomic Marketing Strategy involves systematically assessing the performance of various marketing activities, analyzing data, and generating reports to inform strategic decision-making. The central focus is often on measuring the impact on revenue, allowing businesses to understand the return on investment (ROI) and refine their marketing strategies for optimal results.
- Tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Objective: Monitor and measure relevant KPIs that align with marketing objectives and contribute to revenue generation.
- Implementation: Identify and track KPIs such as website traffic, conversion rates, lead generation, and customer acquisition cost. These metrics provide insights into the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
- Conversion Tracking:
- Objective: Measure the conversion of leads into customers or desired actions that contribute to revenue.
- Implementation: Utilize analytics tools to track conversions from various channels. Understand the customer journey and identify touchpoints that lead to successful conversions.
- Attribution Modeling:
- Objective: Attribute revenue to specific marketing channels or touchpoints to understand their individual contributions.
- Implementation: Implement attribution models to analyze how different marketing efforts contribute to the customer’s decision-making process. This insight helps in optimizing resource allocation.
- Revenue Analytics:
- Objective: Analyze revenue data to understand trends, patterns, and areas for improvement.
- Implementation: Utilize revenue analytics tools to break down revenue by product, channel, or customer segment. This analysis informs strategic decisions related to pricing, product positioning, and target audience.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) Measurement:
- Objective: Understand the long-term value of customers to the business in terms of revenue.
- Implementation: Calculate CLV by assessing the average revenue generated by a customer over their entire relationship with the business. This metric guides marketing strategies for customer retention and loyalty.
- Return on Investment (ROI) Analysis:
- Objective: Evaluate the effectiveness of marketing campaigns by comparing the generated revenue to the cost of the campaign.
- Implementation: Calculate the ROI for each marketing initiative by dividing the revenue generated by the campaign by the cost incurred. This analysis helps in optimizing future marketing spend.
- Sales Funnel Analysis:
- Objective: Assess the efficiency of the sales funnel in converting leads into paying customers.
- Implementation: Analyze the sales funnel stages to identify areas of improvement. Optimize messaging, content, and touchpoints to enhance the conversion rates at each stage.
- A/B Testing and Experimentation:
- Objective: Experiment with variations in marketing strategies to identify the most effective approaches for revenue generation.
- Implementation: Conduct A/B tests on various elements, such as ad copy, landing pages, and email campaigns, to determine which variations lead to higher conversion rates and revenue.
- Customized Reporting:
- Objective: Develop customized reports that provide actionable insights into marketing performance.
- Implementation: Create reports that align with the specific goals and priorities of the business. Customize dashboards to present key metrics and trends in a format that facilitates decision-making.
- Communication of Results:
- Objective: Effectively communicate marketing performance results to key stakeholders within the organization.
- Implementation: Regularly share comprehensive reports highlighting key findings, successes, and areas for improvement. Ensure clear communication of the impact of marketing efforts on overall revenue.
Measuring and reporting in Atomic Marketing Strategy, with a focus on revenue, ensures that businesses have a data-driven understanding of the effectiveness of their marketing initiatives. This information empowers strategic decision-making, enabling continuous optimization for increased revenue and overall business success.
We’ve made a tool Ads Spend Calculator to help you budget your spending.
Make the Most of Your Atomic Marketing Strategy
Remember, each step is interconnected, and success lies in the seamless integration of these components. Regularly assess and adapt your strategy based on performance metrics, market shifts, and evolving customer needs.
By approaching your marketing strategy with this systematic and tool-optimized framework, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape and drive sustainable growth.
How We Keep and Refine Our Atomic Marketing Strategy
We keep all our clients’ Marketing Strategies on Figma-Figjam. This allows us to take a step back and look at the bigger picture.
“Marketing strategy without execution is useless,” as famously quoted by management guru Peter Drucker. In the marketing world, the true value lies not only in the brilliance of the strategy but in the effective implementation of those well-thought-out plans.
Benjamin Franklin once said, “Well done is better than well said.” In other words, the success of a marketing strategy hinges on the meticulous execution of each component. It’s not just about having a roadmap; it’s about navigating the terrain and reaching the destination precisely.
As Thomas Edison aptly said, “Vision without execution is hallucination.” In marketing, turning vision into reality is where the rubber meets the road, and tangible results begin to unfold.
Next Action
Tired of the uphill battle of navigating marketing strategies for the first time? Save precious time and avoid the pitfalls of trial and error. Choose Laman7 as your dedicated marketing arm, and let us streamline your process and deliver marketing services.
With our expertise, you won’t waste a year figuring it out—instead, seize the opportunity for accelerated growth. Elevate your brand efficiently and effectively. Contact us now to transform your marketing journey!






